pacman::p_load(sf, sfdep, tmap, plotly, tidyverse, zoo, Kendall)In Class Exercise 7 - Emerging Hot Spot Analysis: sfdep methods
Importing Packages
Importing Data
hunan <- st_read(dsn = "data/geospatial",
layer = "Hunan")Reading layer `Hunan' from data source
`C:\Users\Daniel\Desktop\Github\IS419\IS415-GAA\In-Class_Ex\In-Class_Ex07\data\geospatial'
using driver `ESRI Shapefile'
Simple feature collection with 88 features and 7 fields
Geometry type: POLYGON
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 108.7831 ymin: 24.6342 xmax: 114.2544 ymax: 30.12812
Geodetic CRS: WGS 84Importing Geospatial Date
hunan <- st_read(dsn = "data/geospatial",
layer = "Hunan")Reading layer `Hunan' from data source
`C:\Users\Daniel\Desktop\Github\IS419\IS415-GAA\In-Class_Ex\In-Class_Ex07\data\geospatial'
using driver `ESRI Shapefile'
Simple feature collection with 88 features and 7 fields
Geometry type: POLYGON
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 108.7831 ymin: 24.6342 xmax: 114.2544 ymax: 30.12812
Geodetic CRS: WGS 84Importing Attribute Table
GDPPC <- read_csv("data/aspatial/Hunan_GDPPC.csv")Creating a Time Series Cube
GDPPC_st <- spacetime(GDPPC, hunan,
.loc_col = "County",
.time_col = "Year")is_spacetime_cube(GDPPC_st)[1] TRUEComputing Gi*
Deriving spatial weights
GDPPC_nb <- GDPPC_st %>%
activate("geometry") %>%
mutate(nb = include_self(st_contiguity(geometry)),
wt = st_inverse_distance(nb, geometry,
scale = 1,
alpha = 1),
.before = 1) %>%
set_nbs("nb") %>%
set_wts("wt")
Note
activate()of dplyr package is used to activate the geometry contextmutate()of dplyr package is used to create two new columns nb and wt.Then we will activate the data context again and copy over the nb and wt columns to each time-slice using
set_nbs()andset_wts()- row order is very important so do not rearrange the observations after using
set_nbs()orset_wts().
- row order is very important so do not rearrange the observations after using
head(GDPPC_nb)# A tibble: 6 × 5
Year County GDPPC nb wt
<dbl> <chr> <dbl> <list> <list>
1 2005 Anxiang 8184 <int [6]> <dbl [6]>
2 2005 Hanshou 6560 <int [6]> <dbl [6]>
3 2005 Jinshi 9956 <int [5]> <dbl [5]>
4 2005 Li 8394 <int [5]> <dbl [5]>
5 2005 Linli 8850 <int [5]> <dbl [5]>
6 2005 Shimen 9244 <int [6]> <dbl [6]>Computing Gi*
gi_stars <- GDPPC_nb %>%
group_by(Year) %>%
mutate(gi_star = local_gstar_perm(
GDPPC, nb, wt)) %>%
tidyr::unnest(gi_star)Mann-Kendall Test
cbg <- gi_stars %>%
ungroup() %>%
filter(County == "Changsha") |>
select(County, Year, gi_star)Plotting result using ggplot2
ggplot(data = cbg,
aes(x = Year,
y = gi_star)) +
geom_line() +
theme_light()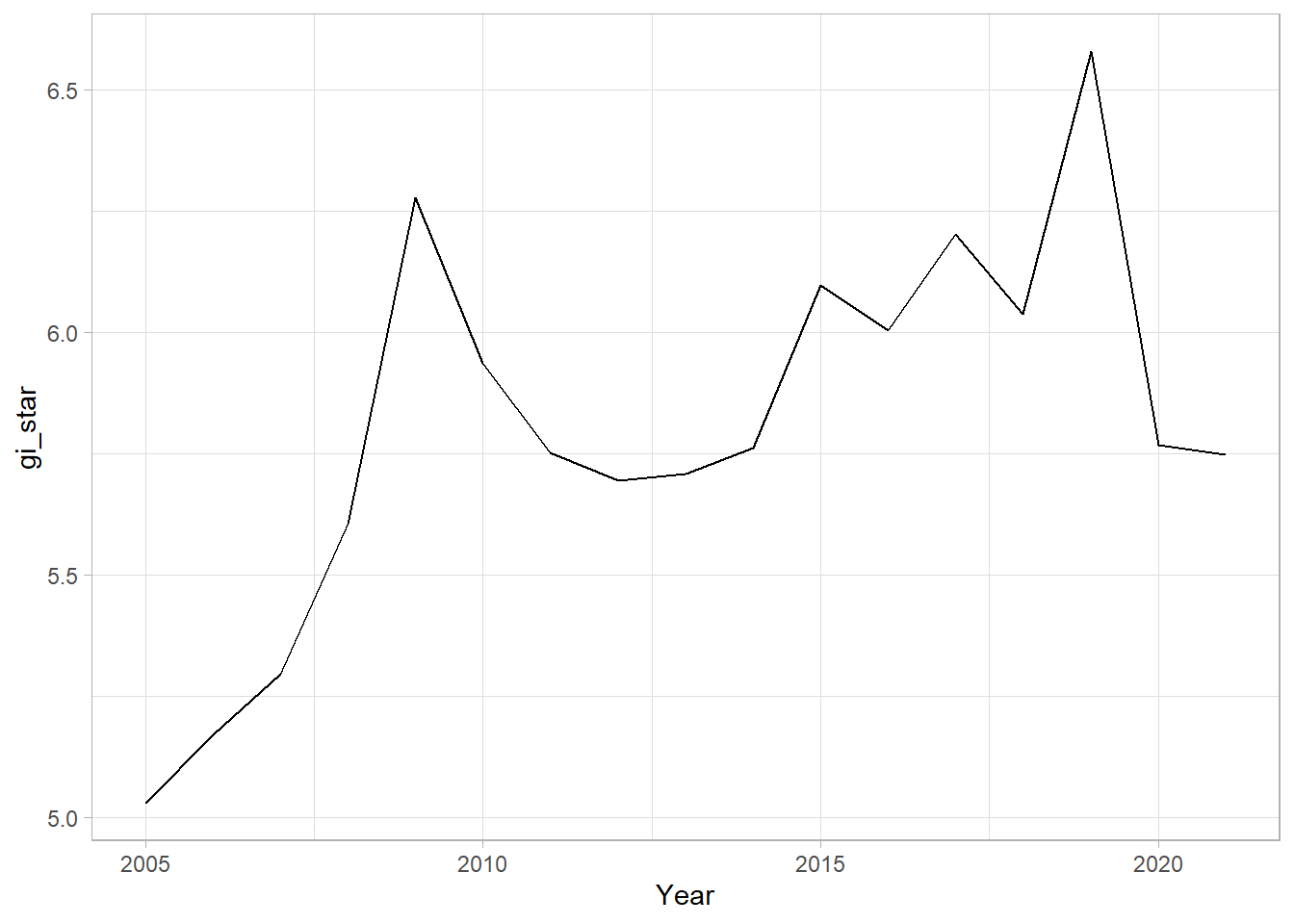
Using plotly package
p <- ggplot(data = cbg,
aes(x = Year,
y = gi_star)) +
geom_line() +
theme_light()
ggplotly(p)In the below result, sl is the p-value. This result tells us that there is a slight upward but insignificant trend.
cbg %>%
summarise(mk = list(
unclass(
Kendall::MannKendall(gi_star)))) %>%
tidyr::unnest_wider(mk)# A tibble: 1 × 5
tau sl S D varS
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 0.485 0.00742 66 136. 589.Using groupby
ehsa <- gi_stars %>%
group_by(County) %>%
summarise(mk = list(
unclass(
Kendall::MannKendall(gi_star)))) %>%
tidyr::unnest_wider(mk)Arrange to show significant emerging hot/cold spots
emerging <- ehsa %>%
arrange(sl, abs(tau)) %>%
slice(1:5)Performing Emerging Hotspot Analysis
ehsa <- emerging_hotspot_analysis(
x = GDPPC_st,
.var = "GDPPC",
k = 1,
nsim = 99
)Visualizing distribution of EHSA Classes
ggplot(data = ehsa,
aes(x = classification)) +
geom_bar()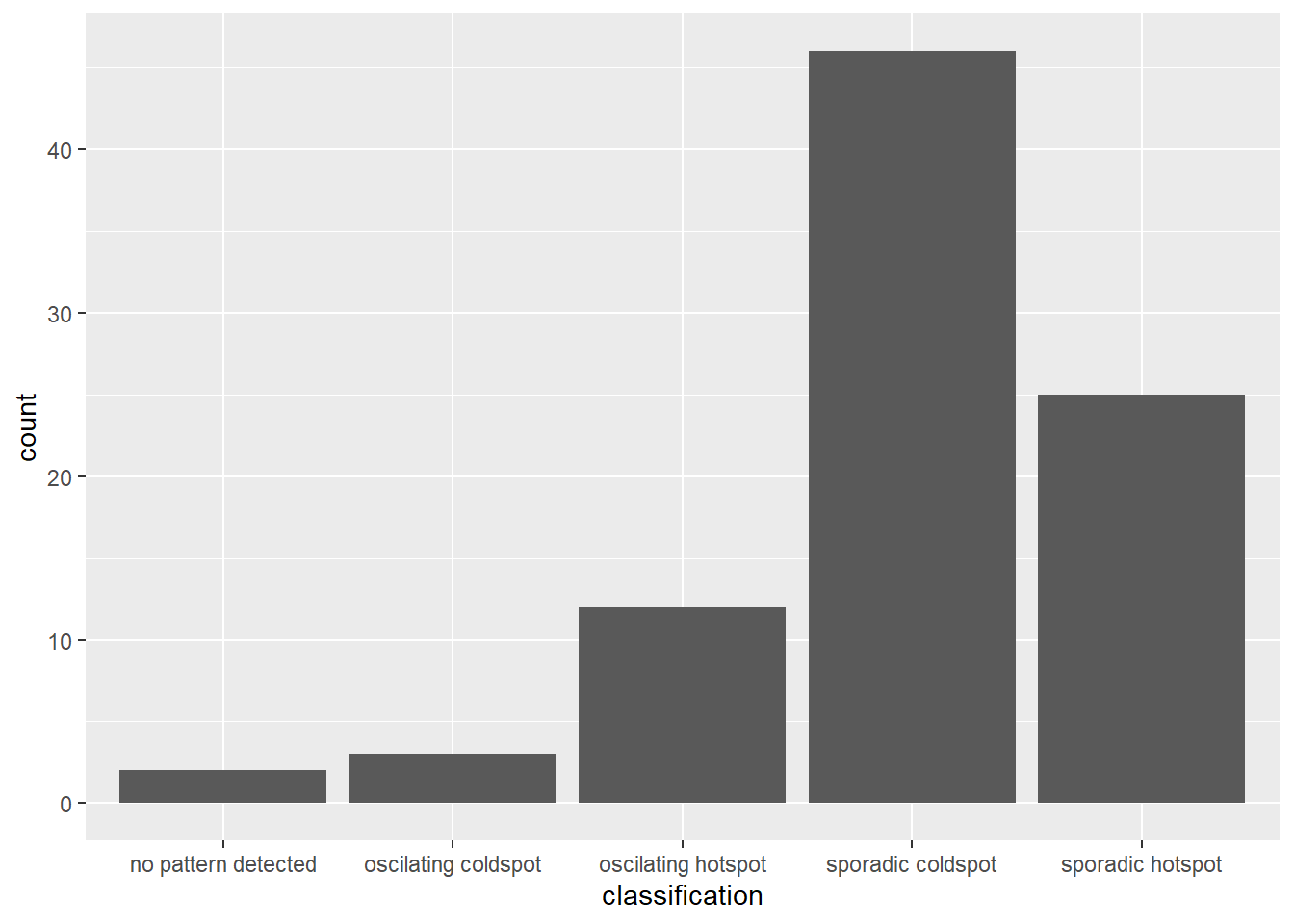
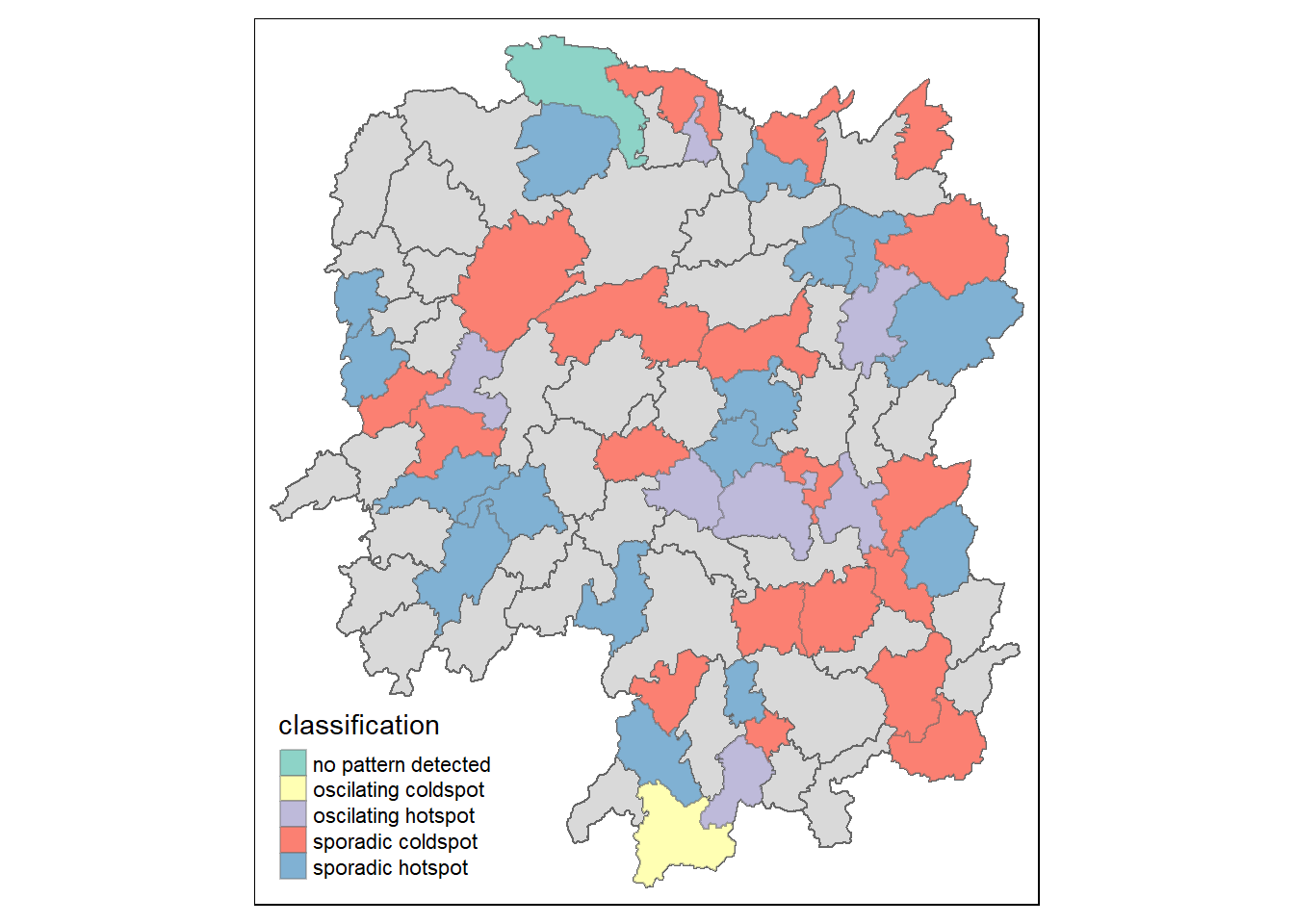
Visualizing EHSA
hunan_ehsa <- hunan %>%
left_join(ehsa,
by = c("County" = "location"))Plotting Categorical Choropleth map
ehsa_sig <- hunan_ehsa %>%
filter(p_value < 0.05)
tmap_mode("plot")
tm_shape(hunan_ehsa) +
tm_polygons() +
tm_borders(alpha = 0.5) +
tm_shape(ehsa_sig) +
tm_fill("classification") +
tm_borders(alpha = 0.4)